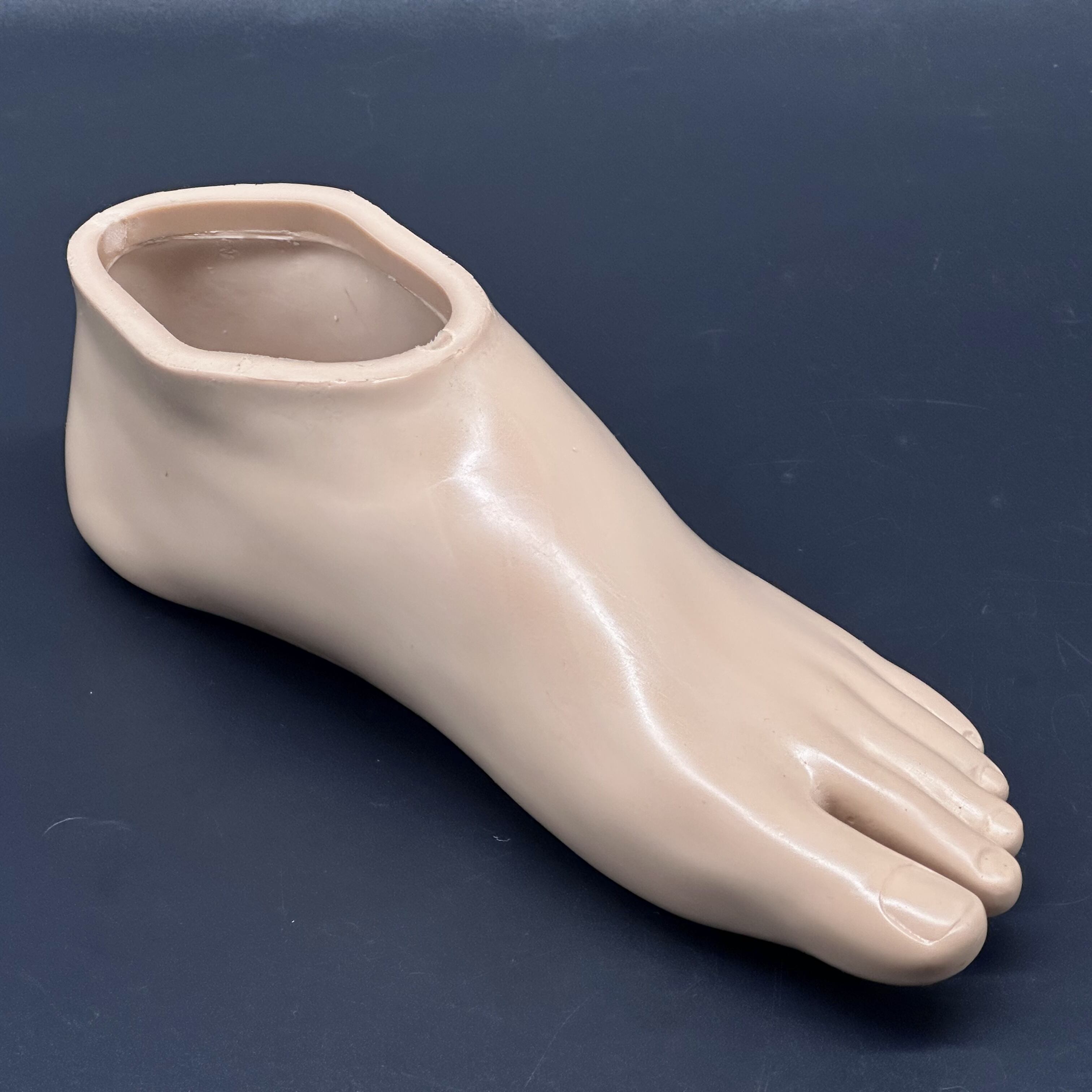
Modern prosthetic technology has revolutionized mobility solutions for individuals with lower limb amputations, with the polyurethane foot emerging as a breakthrough innovation in biomechanical engineering. These advanced prosthetic components combine exceptional durability with sophisticated energy return mechanisms, fundamentally transforming how amputees experience walking, running, and daily activities. The integration of polyurethane materials in prosthetic foot design represents a significant leap forward from traditional rigid components, offering enhanced flexibility and natural gait patterns that closely mimic biological foot function.
The biomechanical advantages of polyurethane prosthetic components stem from their unique material properties and engineered design characteristics. Unlike conventional prosthetic materials, polyurethane exhibits exceptional elasticity and energy storage capabilities, allowing for more efficient energy transfer during the gait cycle. This translates to reduced metabolic expenditure for users, enabling longer periods of activity without excessive fatigue. The material's inherent shock absorption properties also contribute to improved comfort during impact phases of walking, particularly on varied terrain surfaces.
Material Science and Engineering Excellence
Advanced Polymer Composition
The polyurethane foot utilizes cutting-edge polymer chemistry to achieve optimal performance characteristics. The material composition involves carefully balanced molecular chains that provide both flexibility and structural integrity under repeated loading conditions. This molecular architecture enables the prosthetic component to withstand millions of loading cycles while maintaining consistent performance parameters. The engineering team behind these innovations has developed proprietary formulations that enhance tear resistance and fatigue life, ensuring long-term reliability for active users.
Manufacturing processes for polyurethane prosthetic components employ precision molding techniques that create uniform density distribution throughout the foot structure. This consistency ensures predictable mechanical behavior and eliminates weak points that could lead to premature failure. The controlled curing process allows for fine-tuning of material properties, enabling customization based on individual user requirements and activity levels. Quality control measures throughout production guarantee that each polyurethane foot meets stringent performance standards before reaching end users.
Biomechanical Design Principles
The geometric configuration of polyurethane prosthetic feet incorporates biomechanical research findings to optimize energy return efficiency. The toe lever arm length and heel configuration work in harmony to create natural roll-over characteristics that facilitate smooth weight transfer during walking. This design approach minimizes compensatory movements that can lead to secondary complications in the residual limb or adjacent joints. The carefully engineered curvature profiles ensure that ground reaction forces are distributed appropriately throughout the gait cycle.
Finite element analysis plays a crucial role in optimizing the structural design of polyurethane components. Engineers utilize sophisticated computer modeling to predict stress concentrations and deformation patterns under various loading scenarios. This computational approach allows for design refinements that maximize energy storage and return while ensuring structural durability. The iterative design process incorporates feedback from clinical testing to validate theoretical predictions and fine-tune performance characteristics based on real-world usage patterns.
Performance Enhancement Features
Energy Return Mechanisms
The energy return capabilities of polyurethane prosthetic components represent a fundamental advancement in assistive mobility technology. During heel strike and midstance phases, the material compresses and stores mechanical energy that is subsequently released during push-off, providing propulsive assistance to the user. This energy recycling mechanism reduces the metabolic cost of locomotion and enables more natural walking patterns. Clinical studies demonstrate measurable improvements in walking efficiency when comparing polyurethane feet to conventional prosthetic alternatives.
The polyurethane foot incorporates multiple energy storage zones that activate sequentially throughout the gait cycle. The heel region provides initial shock absorption and energy storage during loading response, while the forefoot section stores additional energy during late stance phase. This multi-zone approach maximizes energy return efficiency and creates a more responsive feel for the user. The coordinated energy release timing helps maintain forward momentum and reduces the effort required for swing phase initiation.
Adaptive Flexibility Characteristics
Polyurethane materials exhibit unique adaptive flexibility that responds to varying walking speeds and terrain conditions. At slower walking speeds, the material provides gentle support and controlled motion, while higher activity levels activate increased stiffness characteristics for enhanced energy return. This adaptive behavior eliminates the need for multiple prosthetic components for different activities, providing versatility in a single device. The material's viscoelastic properties contribute to this adaptive response, automatically adjusting to user demands.
The flexibility characteristics of polyurethane prosthetic feet enable natural ankle motion that closely approximates biological function. This range of motion facilitates walking on inclined surfaces and uneven terrain by allowing the foot to conform to ground contours. The controlled flexibility also assists with balance maintenance during standing activities and provides proprioceptive feedback that enhances user confidence. The graduated stiffness distribution throughout the foot structure ensures optimal performance across a wide range of functional activities.
Clinical Benefits and User Outcomes
Gait Efficiency Improvements
Clinical research demonstrates significant improvements in gait efficiency parameters when users transition to polyurethane prosthetic components. Oxygen consumption measurements show reduced metabolic demands during walking activities, allowing users to maintain higher activity levels for extended periods. Gait analysis reveals more symmetric walking patterns with improved temporal parameters compared to conventional prosthetic alternatives. The enhanced efficiency translates to practical benefits including increased walking distances and reduced fatigue during daily activities.
Kinematic analysis of polyurethane foot users reveals normalized joint angle patterns throughout the gait cycle. The energy return characteristics facilitate more natural hip and knee motion, reducing compensatory movements that can lead to long-term complications. Ground reaction force measurements demonstrate improved loading patterns that more closely resemble normal locomotion. These biomechanical improvements contribute to enhanced user satisfaction and quality of life outcomes across diverse populations of prosthetic users.
Balance and Stability Enhancement
The polyurethane foot design incorporates features specifically engineered to enhance balance and stability during static and dynamic activities. The broad base of support and controlled flexibility provide confidence during standing activities and transitions between sitting and standing positions. The material's shock absorption properties reduce sudden perturbations that could compromise balance, particularly on irregular surfaces. This stability enhancement is particularly beneficial for elderly users or those with additional balance challenges.
Proprioceptive feedback mechanisms built into polyurethane prosthetic components contribute to improved balance awareness and postural control. The material's responsiveness provides subtle sensory information about ground contact and weight distribution that users learn to interpret over time. This enhanced feedback loop supports the development of more confident and stable movement patterns. Clinical assessments demonstrate measurable improvements in balance confidence scores and reduced fall risk among polyurethane foot users.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Long-term Performance Reliability
Polyurethane prosthetic components demonstrate exceptional durability under normal usage conditions, with many devices maintaining optimal performance characteristics for multiple years. The material's resistance to fatigue failure ensures consistent energy return properties throughout the device lifespan. Environmental factors such as temperature variations and moisture exposure have minimal impact on polyurethane performance, making these components suitable for diverse climatic conditions. The robust construction reduces the need for frequent replacements and associated healthcare costs.
Accelerated aging tests conducted on polyurethane prosthetic components validate their long-term reliability under simulated high-use conditions. These laboratory evaluations demonstrate maintained flexibility and energy return characteristics after millions of loading cycles. Field studies tracking real-world performance confirm the laboratory findings, with users reporting consistent function throughout extended usage periods. The predictable wear patterns allow for proactive replacement scheduling and minimize unexpected device failures.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
The maintenance requirements for polyurethane prosthetic components are minimal compared to mechanical alternatives, contributing to overall cost-effectiveness and user convenience. Regular cleaning with mild soap and water maintains hygiene and appearance without affecting material properties. Visual inspections for wear patterns or damage can be performed by users as part of routine care protocols. The absence of moving parts eliminates the need for lubrication or mechanical adjustments that are required with other prosthetic technologies.
Professional maintenance intervals for polyurethane prosthetic feet are typically extended compared to conventional devices, reducing healthcare system burden and user inconvenience. Prosthetists can perform comprehensive evaluations during routine follow-up appointments to assess wear patterns and alignment parameters. The predictable performance degradation patterns allow for evidence-based replacement recommendations that optimize both function and cost-effectiveness. User education regarding proper care techniques maximizes device lifespan and maintains optimal performance characteristics.
FAQ
How does a polyurethane foot compare to carbon fiber alternatives in terms of energy return
Polyurethane prosthetic components typically provide more consistent energy return across varying walking speeds compared to carbon fiber alternatives. While carbon fiber feet excel at high activity levels, polyurethane materials offer superior performance at moderate walking speeds that comprise the majority of daily activities. The viscoelastic properties of polyurethane allow for automatic adaptation to different usage scenarios without requiring manual adjustments. Clinical studies indicate that polyurethane feet provide more predictable energy return characteristics, leading to improved user confidence and reduced learning curve for new prosthetic users.
What weight restrictions apply to polyurethane prosthetic foot components
Most polyurethane prosthetic feet are engineered to accommodate users weighing up to 275 pounds while maintaining optimal performance characteristics. The material properties and structural design provide adequate strength margins to ensure safety and durability across this weight range. Heavier users may require specialized versions with enhanced structural reinforcement or alternative material configurations. Weight distribution patterns and activity levels are considered alongside body weight when determining appropriate prosthetic specifications, ensuring optimal matching between user requirements and device capabilities.
Can polyurethane feet be used for high-impact activities like running or sports
Advanced polyurethane prosthetic components are specifically designed to accommodate high-impact activities including running, jumping, and various sports applications. The energy return characteristics actually enhance performance during these activities by providing propulsive assistance during push-off phases. However, activity-specific models may be recommended for optimal performance in particular sports or high-intensity applications. The shock absorption properties of polyurethane materials also provide protection for the residual limb during high-impact activities, reducing stress concentrations that could lead to discomfort or injury.
How long does a polyurethane prosthetic foot typically last before replacement is needed
The typical lifespan of a polyurethane prosthetic foot ranges from 3 to 5 years depending on usage patterns, body weight, and activity levels. Active users who engage in high-impact activities may require replacement sooner, while less active individuals often achieve longer service life. Regular monitoring by healthcare providers helps identify when performance characteristics begin to decline, indicating the need for replacement. The gradual wear patterns of polyurethane materials allow for planned replacement scheduling rather than unexpected failures, contributing to better healthcare planning and cost management.
Table of Contents
- Material Science and Engineering Excellence
- Performance Enhancement Features
- Clinical Benefits and User Outcomes
- Durability and Maintenance Considerations
-
FAQ
- How does a polyurethane foot compare to carbon fiber alternatives in terms of energy return
- What weight restrictions apply to polyurethane prosthetic foot components
- Can polyurethane feet be used for high-impact activities like running or sports
- How long does a polyurethane prosthetic foot typically last before replacement is needed